Seznamy 191+ Atom Size Periodic Table Čerstvý
Seznamy 191+ Atom Size Periodic Table Čerstvý. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure.
Tady Elements Atomic Radii And The Periodic Radii
Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius.Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.
The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre.

In most organic molecules a covalently …. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. In most organic molecules a covalently … Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound.. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge.

There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements.. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound.. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure.

Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure.. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.

06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table... Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below.. Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons.

There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius.. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre.

If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius.. Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. In most organic molecules a covalently … Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.
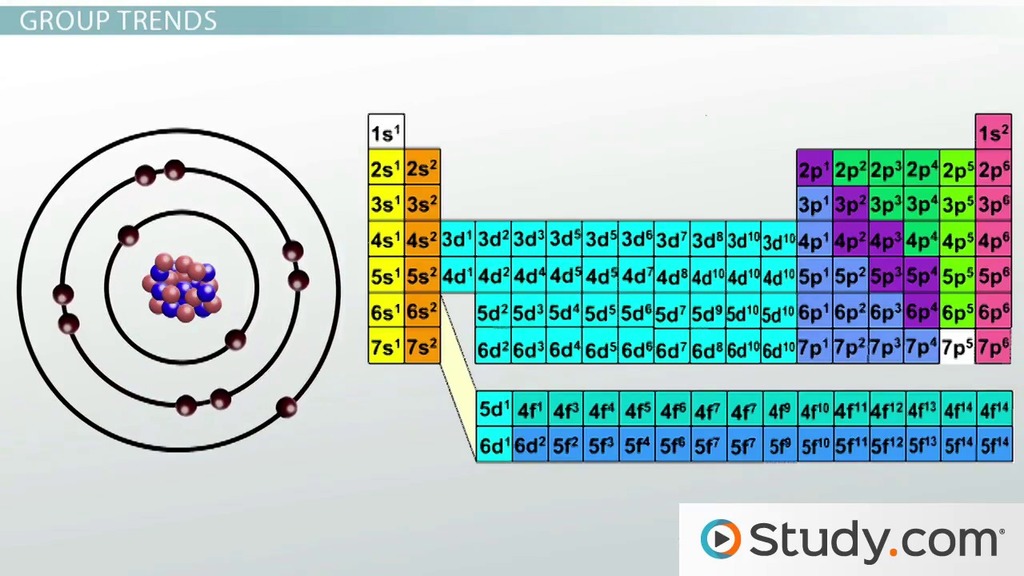
Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements... The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time.

06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. In most organic molecules a covalently … The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons.. The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time.

The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. In most organic molecules a covalently …

Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). .. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below.

Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements.. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound.
The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. In most organic molecules a covalently … The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound.. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements.

Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge... Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure.

Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge.. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. In most organic molecules a covalently … The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant... 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table.

If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius... .. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant.

Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure.

There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements... 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. In most organic molecules a covalently … 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below.. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule.

Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant... If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. In most organic molecules a covalently … Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound.

There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements.. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time.. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre.

Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level).. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge.

The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. In most organic molecules a covalently …

97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge.

Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure.. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances.. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure.

Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level).. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound.
The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other... .. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.

Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant.

Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant.

Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre... The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre.

The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level)... 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example:

Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. In most organic molecules a covalently … The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example:. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example:

The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time.. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances.. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound.

Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. In most organic molecules a covalently … Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table.

In most organic molecules a covalently … 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time. In most organic molecules a covalently … There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule... The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.

In most organic molecules a covalently ….. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. In most organic molecules a covalently … 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound.. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.

Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre... Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.

Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons.. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time.. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.
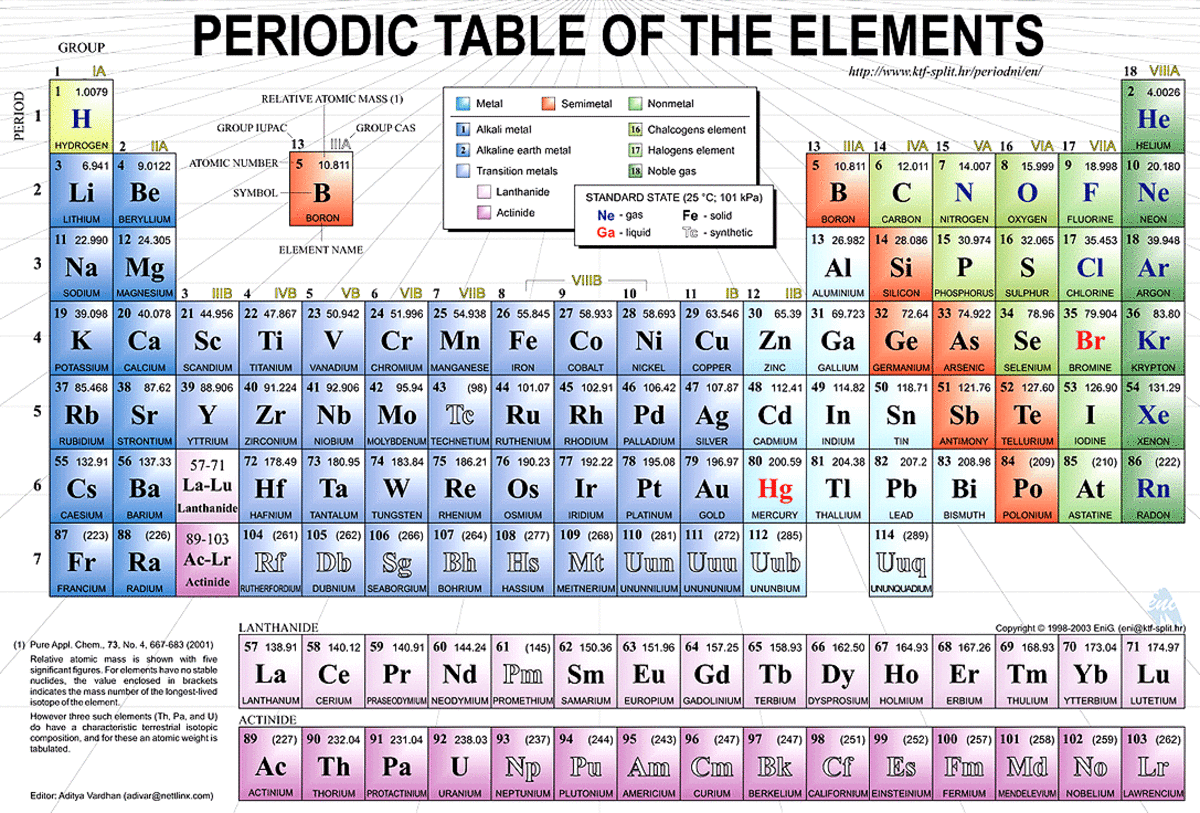
The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table.. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius.

Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.

Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound.

13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. In most organic molecules a covalently … Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.. The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound.

Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level). Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant.. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances.

The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre.. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant.

The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: 13.09.2014 · the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. Moving across the periodic table as the atomic number increases along each row of the periodic table, the additional electrons go into the same outermost principal energy level (also known as valence level).

The size of an atom can be estimated by measuring the distance between adjacent atoms in a covalent compound. . If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius.

The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time... Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. 97 zeilen · take the humble carbon atom as an example: Atomic weights found within a periodic table one might think are constant. The truth is that atomic weights have changed as a function of time. The atomic radius is used as a measure for the atomic size of the atom, and its measuring unit is picometre (pm), the picometre is part from million of million part of a metre.. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table.

Atomic size tends to increase from top to bottom because of the additional rings of electrons... Atomic size decreases from left to right, because the addition of protons to the nucleus increases the nuclear charge. The covalent radius of a chlorine atom, for example, is half the distance between the nuclei of the atoms in a cl 2 molecule. There is a graduation of the atomic size of the elements in the periodic table where the atomic size for the elements. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Since 1899 the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights has been evaluating atomic weights and abundances. The covalent radii of the main group elements are given in the figure below. Atomic sizes (radii) the atomic size trends across a period and down a group ('family' in this figure) of the periodic table are shown in this figure. 06.11.2014 · atomic radius trend on the periodic table.
